A palindrome is a word, phrase, or sequence that reads the same forward and backward. This 8086 assembly program determines whether a given string is a palindrome by reversing the string and comparing it to the original.
The program follows these steps:
- Initialize the Data Segment: Load the string to be checked.
- Reverse the String: Store the reversed string in another memory location.
- Compare the Original and Reversed Strings: Use
CMPSBto compare byte-by-byte. - Print the Result: Display whether the string is a palindrome or not.
DATA SEGMENT BLOCK1 DB 'MALAYALAM' MSG1 DB "IT IS PALINDROME $" MSG2 DB "IT IS NOT PALINDROME $" PAL DB 00H DATA ENDS PRINT MACRO MSG MOV AH,09H LEA DX,MSG INT 21H INT 3H ENDM EXTRA SEGMENT BLOCK2 DB 9 DUP(?) EXTRA ENDS CODE SEGMENT ASSUME CS:CODE,DS:DATA,ES:EXTRA START: MOV AX,DATA MOV DS,AX MOV AX,EXTRA MOV ES,AX LEA SI,BLOCK1 LEA DI,BLOCK2+8 MOV CX,00009H BACK: CLD LODSB STD STOSB LOOP BACK LEA SI,BLOCK1 LEA DI,BLOCK2 MOV CX,0009H CLD REPZ CMPSB JNZ SKIP PRINT MSG1 SKIP: PRINT MSG2 CODE ENDS END START
Step-by-Step Explanation of the Palindrome Checking Process
Data Segment:
- BLOCK1: Stores the input string
'MALAYALAM'. - MSG1: Message
"IT IS PALINDROME $"to be displayed if the string is a palindrome. - MSG2: Message
"IT IS NOT PALINDROME $"to be displayed if the string is not a palindrome. - BLOCK2: A temporary storage array used to store the reversed string.
Code Segment: Initialization
- MOV AX, DATA: Loads the address of the data segment into the AX register.
- MOV DS, AX: Sets the DS register to point to the data segment, allowing access to input data.
- MOV AX, EXTRA: Loads the address of the extra segment (used for reversed storage).
- MOV ES, AX: Sets ES to the extra segment, enabling storage of the reversed string.
Reversing the String
- LEA SI, BLOCK1: Loads the address of the input string into SI (source index).
- LEA DI, BLOCK2+8: Loads the address of the last position of BLOCK2 (for reverse storage).
- MOV CX, 00009H: Sets CX register to 9 (length of the string).
- Loop to Reverse the String:
- CLD: Clears the direction flag to process memory forward.
- LODSB: Loads a byte from BLOCK1 into AL.
- STD: Sets the direction flag to decrement DI (storing in reverse).
- STOSB: Stores the loaded byte into BLOCK2 at the current DI position.
- LOOP BACK: Decrements CX and repeats until the entire string is reversed.
Comparing the Original and Reversed Strings
- LEA SI, BLOCK1: Resets SI to the start of BLOCK1.
- LEA DI, BLOCK2: Resets DI to the start of BLOCK2.
- MOV CX, 0009H: Resets CX to the length of the string.
- CLD: Clears the direction flag to compare forward.
- REPZ CMPSB: Compares the original and reversed strings byte by byte.
- JNZ NOT_PALINDROME: If a mismatch is found, jump to print
"IT IS NOT PALINDROME".
Displaying the Result
- PRINT MSG1: If strings match, print
"IT IS PALINDROME". - PRINT MSG2: If strings don’t match, print
"IT IS NOT PALINDROME".
Program Termination
INT 3: Generates an interrupt 3, which typically halts program execution.
EXTRA SEGMENT: Temporary Storage for Reversed String
The EXTRA SEGMENT is used to store the reversed version of the input string.
BLOCK2 DB 9 DUP(?) – Defines a 9-byte storage area using the DUP(?) directive. ? means the memory is uninitialized (will be filled during execution). It is used to store the reversed string.
The EXTRA SEGMENT is assigned to ES (Extra Segment Register) to store the reversed string while processing.
PRINT MACRO MSG: Displaying Messages
The PRINT macro is used to display output messages (either "IT IS PALINDROME" or "IT IS NOT PALINDROME").
Explanation:
- MACRO Definition:
PRINT MACRO MSG: This defines a macro calledPRINT, which takes an argumentMSG(the message to be displayed). - MOV AH, 09H: Loads
AHwith09H, which is a DOS function for printing a string. - LEA DX, MSG: Loads the address of the message into
DXso it can be displayed. - INT 21H: Calls DOS interrupt 21H, which prints the message stored at
DX. - INT 3H: Calls interrupt 3H, which stops program execution.
Flowchart
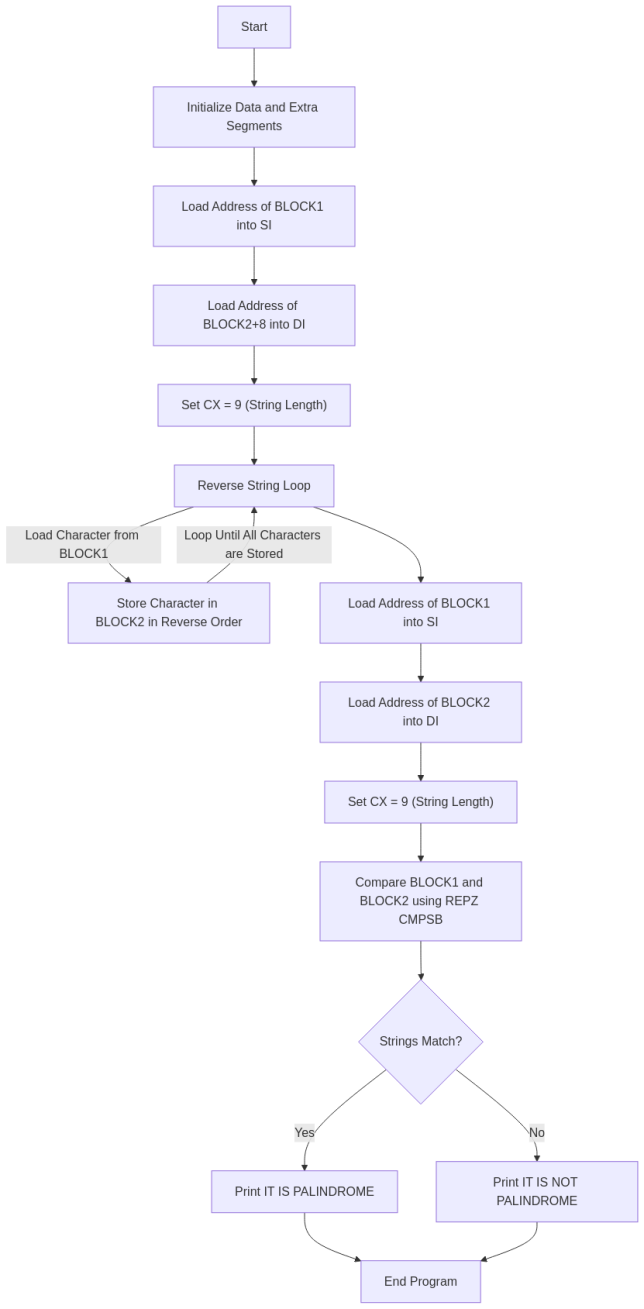
Output
C:\TASM>masm AMPE7.asm
Microsoft (R) Macro Assembler Version 5.00
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corp 1981-1985, 1987. All rights reserved.
Object filename [AMPE7.OBJ]:
Source listing [NUL.LST]:
Cross-reference [NUL.CRF]:
49534 + 414818 Bytes symbol space free
0 Warning Errors
0 Severe Errors
C:\TASM>link AMPE7.obj
Microsoft (R) Overlay Linker Version 3.60
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corp 1983-1987. All rights reserved.
Run File [AMPE7.EXE]:
List File [NUL.MAP]:
Libraries [.LIB]:
LINK : warning L4021: no stack segment
C:\TASM>debug AMPE7.exe
-g
IT IS PALINDROME
AX=0924 BX=0000 CX=0000 DX=0009 SP=0000 BP=0000 SI=0009 DI=0009
DS=14A4 ES=14A8 SS=14A4 CS=14A9 IP=0033 NV UP EI PL ZR NA PE NC
14A9:0033 CC INT 3
-d 14A4:0000
14A4:0000 4D 41 4C 41 59 41 4C 41-4D 49 54 20 49 53 20 50 MALAYALAMIT IS P
14A4:0010 41 4C 49 4E 44 52 4F 4D-45 20 24 49 54 20 49 53 ALINDROME $IT IS
14A4:0020 20 4E 4F 54 20 50 41 4C-49 4E 44 52 4F 4D 45 20 NOT PALINDROME
14A4:0030 24 00 00 00 00 00 00 00-00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 $...............
14A4:0040 4D 41 4C 41 59 41 4C 41-4D 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 MALAYALAM.......
14A4:0050 B8 A4 14 8E D8 B8 A8 14-8E C0 8D 36 00 00 8D 3E ...........6...>
14A4:0060 08 00 B9 09 00 FC AC FD-AA E2 FA 8D 36 00 00 8D ............6...
14A4:0070 3E 00 00 B9 09 00 FC F3-A6 75 09 B4 09 8D 16 09 >........u......
*/
The program executes successfully and prints “IT IS PALINDROME”, meaning the input string (MALAYALAM) is a palindrome.
This assembly program successfully checks if a string is a palindrome by reversing and comparing it with the original. It utilizes fundamental string operations in 8086 assembly to achieve this efficiently.

Madarchod, explanation kidhr hai?
TRanslation:
Motherfucker, where is the explanation?
good work thank you so much
Can you provide flowchart?